Special Purpose Exit Company (SPEC)
STXBP1-NDD Therapeutics
The STXBP1 gene is involved in coordinating the release of synaptic vesciles during neurotransmission and variations thoughout the gene can cause Neurological Development Disorders (NDD) that manifest as epilepsy, intellectual disability, and/or developmental delay.
Genetic Medication Need
Originally identified as casual for Ohtahara Syndrome, a range of other phenotypes have been reported (Dravet, Rett, Lennox-Gastaut, West syndromes, as well as Infantile Spasms Syndrome and Early Myoclonic Epileptic Encephalopathy (STXBP1 Genereviews). A variety of phenotypic presentations in the patients are observed starting with most frequently Developmental Delay, which is followed by Intellectual Disability, Seizures, Movement Disorders and Neurobehavioral Disorders. With 25% of patients being refractory where current drugs are ineffective for treating their epilepsy and associated phenotypes, there is a significant need for new medications to help overcome the neurological and neuromuscular challenges of STXBP1-associated disorders.
Population Frequency:
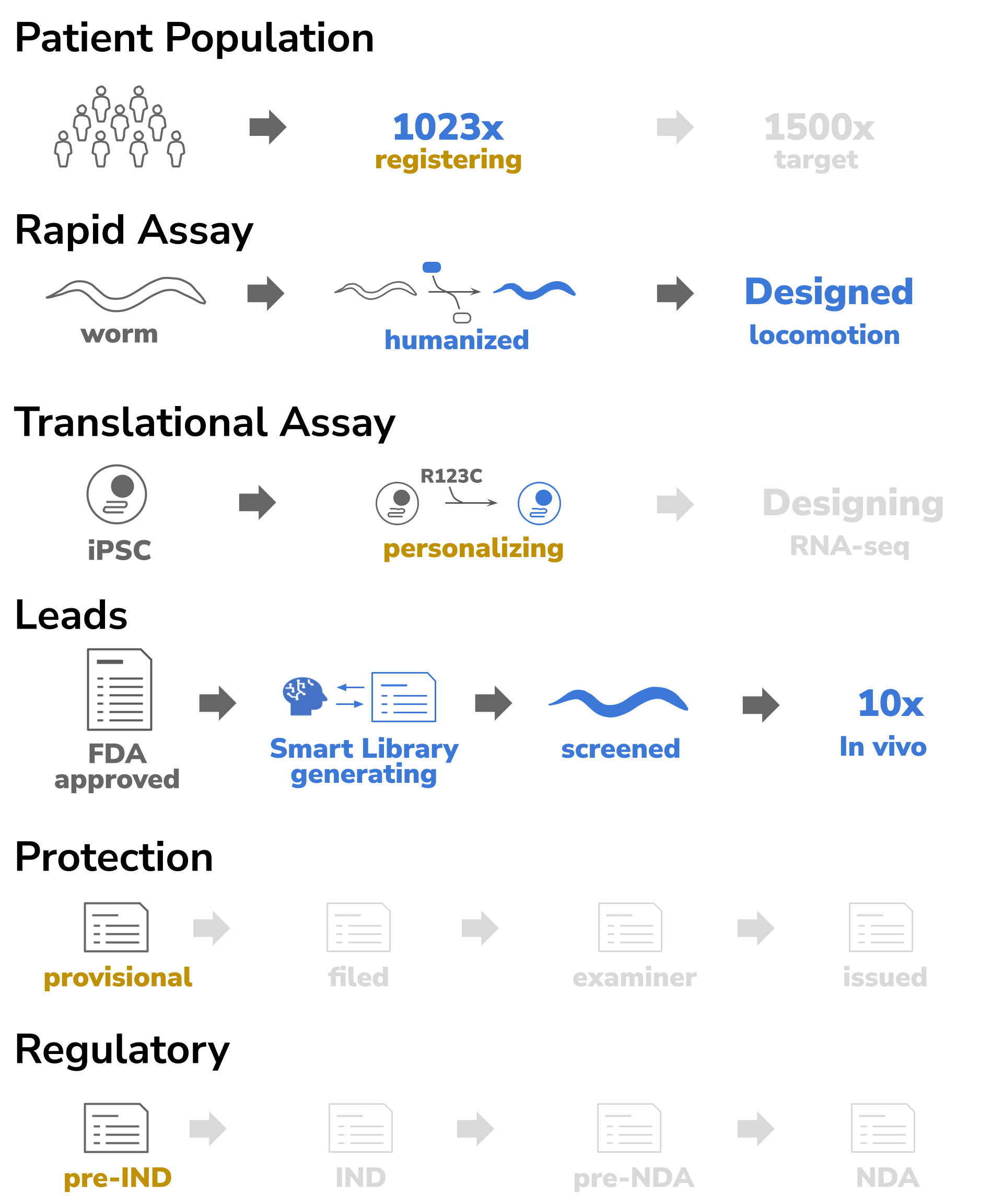
In general epilepsy occurs in about 1% of the adult population and about 0.5% in pediatric (CDC Facts and stats). However on a STXBP1 specific basis, epilepsy and its associated phenotypes are quite rare and occur at 1/30,000 frequency (PMID: 38015929). STXBP1 Foundation recently reported achieving a patient registry of 1023 individuals. Yet statistically, another 265,000 persons on the planet remain undiagnosed for molecular deficit in STXBP1, which indicates the current registry is only 0.5% of its full market potential.
Currently Varsome has 958 variants which we have binned into 3 categories: Pathogenic, Benign, and Variants of uncertain Significance (VUS). AlphaMissense predicts these existing calls are pathogenic for 61% of the VUS. AlphaMissense also predicts that for the entire protein, 64% of all possible single amino acid changes are pathogenic, yet Varsome has only documented 15.5% of these. As a result, we can expect continued growth in achieving additional members to the patient population registry.
Distribution of Variants in STXBP1
Rapid Assay:
A rapid assay has been developed by InVivo Biosystems using whole-gene humanized C elegans (PMID 36411139). In addition to the two most common pathogenic variants (R406H and R292C), InVivo Biosystems made 78 more variants. For all of these variants, we characterized their phenotypic consequences (PMID 38827422). A wide spectrum of locomotion differences were seen in the whole-gene humanized animals.
Landscape of STXBP1 Phenotypes in Animal Models
As a result, the effects of STXBP1 deficiency can be easily monitored measuring locomotion differences. The team at InVivo examined the ability of drugs to restore normal locomotion in R406H and R292C animals. For R406H a 50% hit rate was achieved, while for R292C a 33% hit rate was achieved.
Drug Screening Activity in Animal Models
Translational Assay:
iPSCs can be used to create cortical neurons and detect synaptic deficiencies (PMID: 38242131). STXBP1 may be critical for proper neuron development - Loss of function in STXBP1 can lead to developmental delay at the stages of neurite outgrowth to early synaptogenesis (PMID: 36257704). As a result synaptogenesis markers can be used as endpoints. One of the most pronounced is a dramatic drop in syntaxin levels in the absence of STXBP1. As a result a translational assay in iPSC that monitors changes in syntaxin levels will provide readout of a drug’s ability to restore normal neuronal development activity. To confirm at a physiological level, the drug activity for restoring syntaxin levels can also be screened for its ability to restore normal neurite outgrowth rates.
Activity in Human iPSC Models.
Drugs
Ten compounds were identified in the Rapid Assay - 5x for R406H and 5x for R292C. These compounds were identified from a list of FDA-approved compounds. We will be starting the process of exploring an IND application with one or more of these drugs. We plan to use the 505b2 pathway that allows for accelerated approval on repurposed drugs when applied to a new indication. For proprietary protection, we plan to explore adjustment of formulation and administration routes.
STXBP1-NDD Variants
List of STXBP1 variants repeatedly associated with epilepsy:
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.124T>C (p.Ser42Pro)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.328T>C (p.Cys110Arg)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.416C>T (p.Pro139Leu)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.560C>T (p.Pro187Leu)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.568C>T (p.Arg190Trp)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.704G>A (p.Arg235Gln)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.734A>G (p.His245Arg)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.847G>A (p.Glu283Lys)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.862T>C (p.Trp288Arg)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.874C>T (p.Arg292Cys)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.875G>A (p.Arg292His)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1003C>T (p.Pro335Ser)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1060T>C (p.Cys354Arg)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1061G>A (p.Cys354Tyr)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1216C>T (p.Arg406Cys)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1217G>T (p.Arg406Leu)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1217G>A (p.Arg406His)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1277T>C (p.Leu426Pro)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1439C>T (p.Pro480Leu)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1630G>T (p.Gly544Cys)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1631G>T (p.Gly544Val)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1631G>A (p.Gly544Asp)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1651C>T (p.Arg551Cys)
NM_001032221.6(STXBP1):c.1651C>A (p.Arg551Ser)
Special Purpose Exit Company (SPEC)
Devinebio creates entities (SPECs) to develop drug assets for a specific indications. Five areas are monitored per each SPEC: population, biomarkers, leads, IP, and regulatory. A SPEC’s assets are moved through the milestones of preIND, IND, preNDA and NDA. As a drug asset progresses, it becomes de-risked and it increases in value. Once a drug asset has achieved IND-enabled status, it will have matured enough to be ready for partnering with Pharma.